Podiatry, a specialized branch of medicine focusing on the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of conditions affecting the feet, ankles, and lower extremities, plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health and mobility. This article delves into the scope of podiatry, the role of podiatrists, common foot and ankle conditions treated, and the importance of seeking professional care for foot health.
Podiatrists, also known as podiatric physicians or foot doctors, are healthcare professionals trained specifically in podiatric medicine and surgery. They undergo rigorous education and clinical training, which typically includes obtaining a Doctor of Podiatric Medicine (DPM) degree from an accredited podiatric medical schools. Podiatry Richmond is licensed to diagnose and treat a wide range of foot and ankle conditions, perform surgical procedures, prescribe medications, and provide preventive care and education to patients.
The scope of podiatry encompasses the comprehensive care of the lower extremities, addressing conditions that affect the feet, ankles, and related structures. Podiatrists diagnose and treat various foot ailments, including but not limited to, heel pain (such as plantar fasciitis), bunions, corns, calluses, ingrown toenails, fungal infections, and diabetic foot complications. They also manage injuries such as fractures, sprains, and strains, as well as chronic conditions like arthritis and neuropathy that impact foot health.
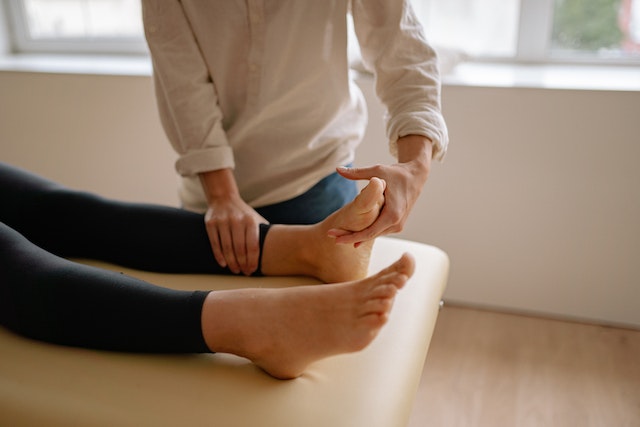
One of the primary roles of podiatrists is to provide preventive care and education to patients, promoting optimal foot health and reducing the risk of future problems. They conduct routine foot examinations to assess the biomechanics, structure, and function of the feet and ankles. By identifying potential issues early, podiatrists can recommend appropriate interventions, such as orthotic devices, footwear modifications, or lifestyle adjustments, to prevent the development or progression of foot conditions.
Podiatric treatment approaches vary depending on the specific condition and its severity. Non-invasive treatments often include conservative measures such as physical therapy, custom orthotics or shoe inserts, medication for pain relief or infection control, and recommendations for home care. For more complex or advanced conditions, podiatric surgery may be recommended to correct deformities, repair injuries, or alleviate chronic pain that does not respond to conservative therapies.
Podiatric surgery encompasses a range of procedures aimed at addressing structural abnormalities, correcting injuries, and restoring function to the feet and ankles. Common surgical interventions performed by podiatrists include bunionectomy (removal of a bunion), hammertoe correction, heel spur removal, tendon repair, joint fusion or replacement, and fracture fixation. Podiatric surgeons undergo specialized training to perform these procedures safely and effectively, often in outpatient settings with minimal recovery time.

Diabetic foot care is a critical aspect of podiatry, given the potential complications associated with diabetes that affect the feet. Diabetes can impair circulation and nerve function, leading to reduced sensation (neuropathy), poor wound healing, and increased susceptibility to infections and ulcers. Podiatrists play a vital role in monitoring and managing diabetic foot health, conducting regular screenings, providing education on proper foot care techniques, and addressing any foot-related complications promptly to prevent serious consequences.
Sports podiatry is another specialized area within podiatry that focuses on the foot and ankle health of athletes and active individuals. Sports podiatrists are trained to diagnose and treat sports-related injuries, biomechanical issues, and overuse conditions that affect performance and mobility. They may recommend customized orthotics, footwear modifications, and rehabilitation programs tailored to the specific demands of various sports and activities, helping athletes maintain optimal foot function and prevent injuries.















